Introduction
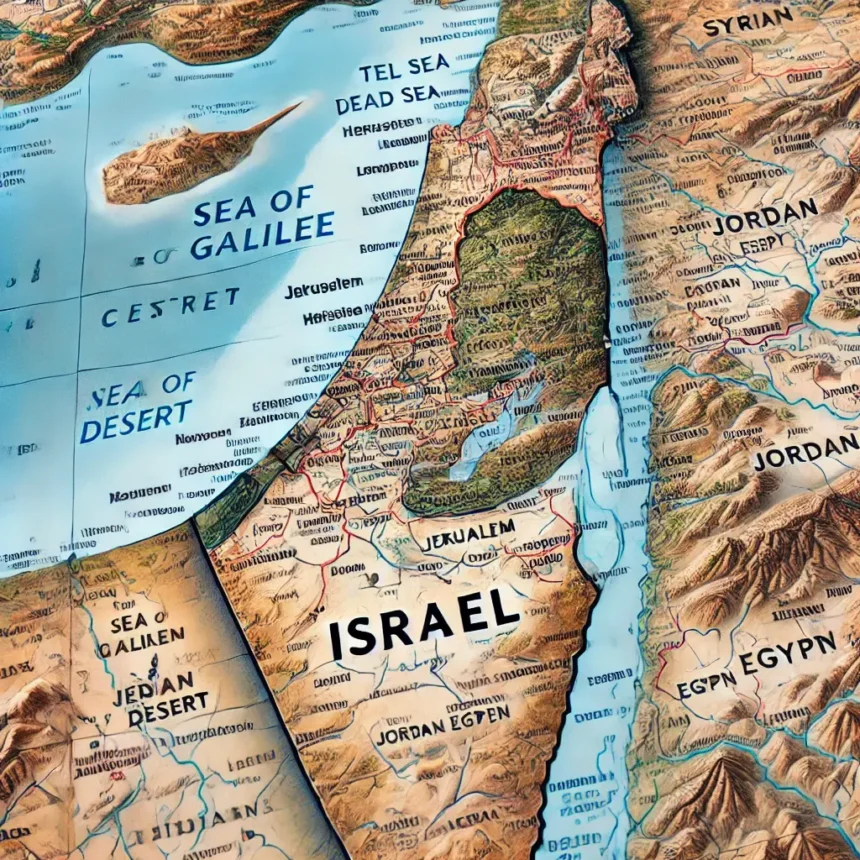
The Israel map is a fascinating depiction of a nation rich in history, culture, and diverse landscapes. Situated in the Middle East, Israel borders Lebanon to the north, Syria to the northeast, Jordan to the east, and Egypt to the southwest. The Mediterranean Sea graces the country’s western edge, offering beautiful coastal cities and scenic landscapes. For anyone interested in learning more about this remarkable nation, understanding the key elements of the Israel map is essential.
Location and Borders
Israel is a small but geopolitically significant country. Its location at the crossroads of Europe, Asia, and Africa gives it a unique status in world affairs. The Israel map clearly outlines its borders:
- Lebanon: To the north of Israel.
- Syria: Northeast of Israel, where the Golan Heights are situated.
- Jordan: To the east, with the Jordan River forming a natural border.
- Egypt: South of Israel, connected through the Negev Desert.
These boundaries play a crucial role in the country’s historical and political context.
Major Cities on the Israel Map
- Jerusalem: The capital of Israel, known for its religious significance to Judaism, Christianity, and Islam.
- Tel Aviv: Located on the Mediterranean coastline, Tel Aviv is Israel’s financial hub and a center for innovation and culture.
- Haifa: A major port city in the northern part of the country.
- Eilat: Israel’s southernmost city on the Red Sea, a popular destination for tourists.
Each of these cities has its unique historical and cultural importance, making the Israel map a dynamic representation of modern civilization coexisting with ancient heritage.
Israel’s Natural Features
The Israel map displays diverse geographical features. From deserts to mountain ranges, the country offers varied landscapes despite its small size. Key features include:
- The Negev Desert: Stretching across southern Israel, the desert is home to unique wildlife and stunning geological formations.
- The Dead Sea: Famous for being the lowest point on Earth, the Dead Sea is known for its high salt content and mineral-rich waters.
- The Sea of Galilee: A freshwater lake in the northern region, significant in Christian history.
- The Jordan River: Flowing from the Sea of Galilee to the Dead Sea, forming part of the border with Jordan.
These natural features define much of Israel’s topography and play a significant role in its climate and biodiversity.
Political and Historical Context of Israel Map
The Israel map has evolved over time due to various geopolitical events. Since its establishment in 1948, the country’s boundaries have been shaped by wars, peace treaties, and negotiations. Key historical moments include:
- 1948 Arab-Israeli War: After the creation of Israel, its borders were immediately contested by neighboring Arab states.
- 1967 Six-Day War: Israel captured significant territories including the West Bank, Gaza Strip, Golan Heights, and the Sinai Peninsula.
- Peace Agreements: Over the years, peace agreements with Egypt and Jordan have altered the Israel map in terms of recognized borders.
Understanding the historical evolution of the Israel map is essential to grasp the modern-day political dynamics of the region.
Key Regions on Israel Map
- West Bank: A landlocked territory in the eastern part of Israel, west of the Jordan River. It is a subject of ongoing conflict between Israel and Palestine.
- Gaza Strip: A coastal region along the Mediterranean, primarily controlled by the Palestinian authority.
- Golan Heights: Located in the northeastern part of Israel, the Golan Heights were captured from Syria during the Six-Day War and remain a strategically significant area.
These regions are crucial to the geopolitical understanding of the Israel map and the ongoing peace processes in the Middle East.
Tourism and Landmarks on Israel Map
Israel attracts millions of tourists every year, largely due to its historical and religious sites. Major tourist destinations visible on the Israel map include:
- The Old City of Jerusalem: Home to the Western Wall, Church of the Holy Sepulchre, and Al-Aqsa Mosque.
- Masada: An ancient fortress situated on a plateau overlooking the Dead Sea.
- Bahá’í Gardens in Haifa: A UNESCO World Heritage Site.
- The Red Sea: Offering opportunities for diving and snorkeling in Eilat.
The Israel map is not just a tool for navigation but a window into the rich cultural and historical treasures the country holds.
Climate Zones on Israel Map
Despite its small size, Israel has several distinct climate zones:
- Mediterranean Climate: Found along the coast, including Tel Aviv and Haifa, characterized by hot, dry summers and mild, wet winters.
- Desert Climate: Predominates in the southern Negev Desert region, with extreme heat during the day and cooler nights.
- Mountain Climate: In higher elevations like Jerusalem, offering cooler temperatures compared to the coastal plains.
These diverse climates are clearly visible when studying the Israel maps, which outlines varying weather conditions across the nation.
Transportation and Infrastructure
Israel’s well-developed infrastructure is essential for its growing economy. The Israel maps shows a network of highways, railways, and airports:
- Ben Gurion Airport: The main international gateway, located near Tel Aviv.
- Railway Lines: Connecting major cities like Jerusalem, Tel Aviv, and Haifa.
- Road Networks: A comprehensive system of highways links different regions, from the bustling cities to remote areas like the Negev Desert.
The Israel maps reflects how the country’s transportation infrastructure supports both domestic travel and international tourism.
Strategic Importance of Israel Map
Israel’s location makes it strategically important not only for the Middle East but for the world at large. The Israel_maps shows its proximity to Europe, Asia, and Africa, highlighting its role as a bridge between these continents. Additionally, Israel’s access to both the Mediterranean and Red Sea makes it a key player in international trade and security.
Education and Research Using Israel Map
Many institutions use the Israel_map for research and education. Mapping technologies in Israel are highly advanced, and the country is a leader in geographic information systems (GIS). Students and researchers analyze the Israel_maps for studies related to history, politics, geography, and environmental sciences.
FAQs About Israel Map
1. What is the size of Israel on the map?
Israel covers approximately 22,145 square kilometers, making it a small country in size.
2. Where is Jerusalem located on the Israel_map?
Jerusalem is centrally located, slightly to the east of the Mediterranean coastline.
3. What bodies of water are shown on the Israel_maps?
The Mediterranean Sea, the Sea of Galilee, the Dead Sea, and the Red Sea are key water bodies on the Israel_maps.
4. What are the main natural features visible on the Israel_map?
Notable features include the Negev Desert, Jordan River, and the Dead Sea.
5. How has the Israel_maps changed over time?
The Israel_maps has evolved through wars, treaties, and negotiations, especially since the establishment of the state in 1948.
Conclusion
The Israel_map offers an intricate look into a country with deep historical roots, significant geographical landmarks, and complex political boundaries. From the bustling streets of Tel Aviv to the ancient city of Jerusalem, every inch of the Israel_map tells a story of the nation’s past, present, and future. Whether you’re a traveler, student, or researcher, the Israel_maps serves as a vital tool in understanding the diverse aspects of this remarkable nation.