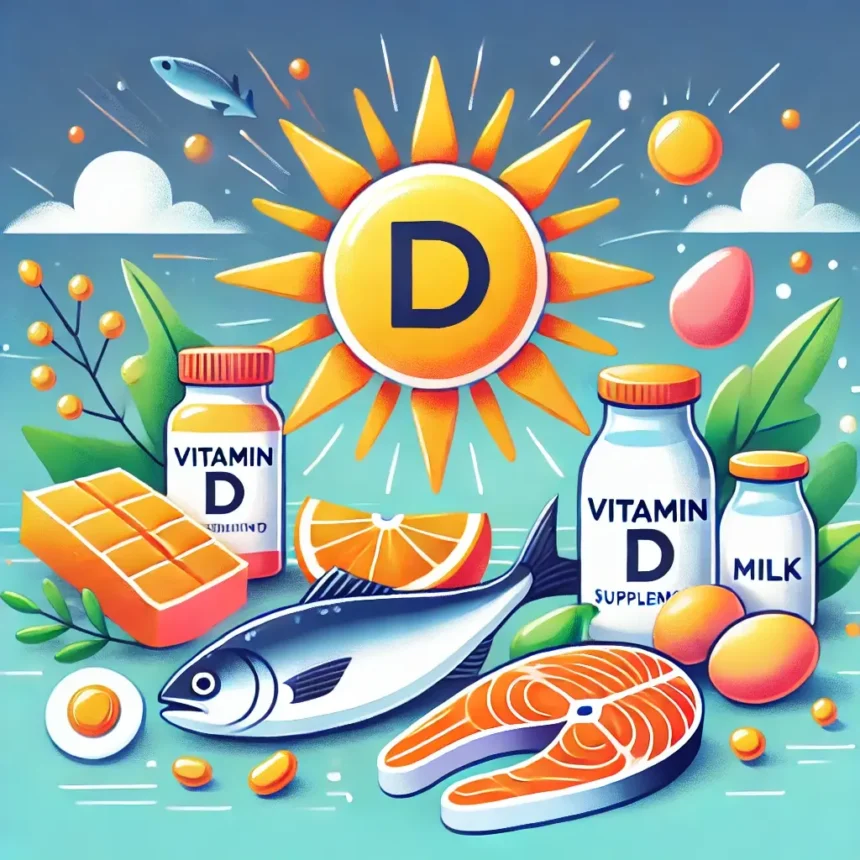
Introduction to Vitamin D
Vitamina d, the “sunshine vitamin,” is essential for maintaining overall health. It is critical in supporting bone health, boosting the immune system, and regulating mood. Our body primarily produces Vitamin D when our skin is exposed to sunlight, but we can also get it from certain foods and supplements.
Getting enough vitamin D is essential for people of all ages. This article will explore Vitamin D’s benefits, sources, and how much you need to stay healthy.
What is Vitamin D?
Vitamin D is a fat-soluble vitamin that helps the body absorb calcium and phosphorus—two minerals essential for bone health. Without enough Vitamin D, bones can become weak and brittle, increasing the risk of osteoporosis.
There are two primary forms of Vitamin D:
- Vitamin D2 (ergocalciferol) – Found in plants, such as mushrooms.
- Vitamin D3 (cholecalciferol) – Found in animal-based foods, such as fish and egg yolks, and is produced by the skin when exposed to sunlight.
Both forms are essential for maintaining healthy levels of vitamin D.
Why is Vitamin D Important for Your Health?
Vitamin D offers a wide range of health benefits. Here are some of the most important reasons to ensure you’re getting enough:
- Supports Bone Health
- Vitamin D helps the body absorb calcium, essential for strong bones and teeth. Without enough Vitamin D, calcium cannot be adequately absorbed, leading to bone problems like rickets in children and osteoporosis in adults.
- Boosts Immune Function
- Vitamin D plays a vital role in strengthening the immune system. It helps the body fight off infections, including the common cold and flu. Studies have shown that people with low Vitamin D levels are more susceptible to infections.
- Improves Mood and Reduces Depression
- Vitamin D is believed to play a role in regulating mood and warding off depression. Low levels of Vitamin D have been linked to an increased risk of mood disorders, including seasonal affective disorder (SAD).
- Supports Heart Health
- Vitamin D may contribute to a healthy cardiovascular system by supporting normal blood pressure levels and reducing the risk of heart disease.
How to Get Enough vitamina d
There are three main ways to ensure you’re getting enough Vitamin D:
- Sunlight Exposure
- Spending time outside in the sun is the most natural way to get Vitamin D. Just 10-30 minutes of sun exposure a few times a week can provide your body with what it needs. However, skin tone, age, and geographic location can affect how much vitamin D your body produces.
- Foods Rich in Vitamin D
- While not many foods naturally contain Vitamin D, there are still some good options:
- Fatty fish like salmon, mackerel, and sardines
- Egg yolks
- Fortified foods, such as milk, orange juice, and cereals
- Mushrooms are exposed to sunlight.
- Vitamin D Supplements
- Supplements are a safe and effective way to boost your levels if you’re not getting enough vitamin D from sunlight and food. Speak to a healthcare provider to determine the proper dosage for your needs.
Who is at Risk of vitamina d Deficiency?
Certain groups of people are more likely to have low levels of Vitamin D:
- People with Limited Sun Exposure
- If you spend most of your time indoors or live in an area with long winters, you may need more sunlight to produce Vitamin D.
- Older Adults
- As we age, our skin produces Vitamin D from sunlight less efficiently. Additionally, older adults often spend less time outdoors.
- People with Darker Skin
- Melanin, the pigment responsible for skin color, can reduce the skin’s ability to produce Vitamin D. Individuals with darker skin may require more sun exposure to maintain healthy Vitamin D levels.
- People with Certain Medical Conditions
- Some health conditions, such as Crohn’s, celiac, and kidney disease, can affect the body’s ability to absorb vitamin D from food and supplements.
How Much vitamina d Do You Need?
The amount of Vitamin D you need depends on several factors, including age, skin color, and how much sun exposure you get. Here are the general recommendations:
- Infants (0-12 months): 400 IU per day
- Children (1-18 years): 600 IU per day
- Adults (19-70 years): 600 IU per day
- Adults (70+ years): 800 IU per day
- Pregnant and breastfeeding women: 600 IU per day
However, some people may need more Vitamin D, especially if they are at risk of deficiency.
Signs of Vitamin D Deficiency
If you’re not getting enough Vitamin D, you may experience the following symptoms:
- Fatigue
- Bone pain or muscle weakness
- Frequent infections
- Depression or low mood
In severe cases, Vitamin D deficiency can lead to bone deformities in children (rickets) or bone weakness in adults (osteomalacia).
Can You Have Too Much Vitamin D?
While Vitamin D is essential for health, it’s also possible to have too much of it. Excess Vitamin D can lead to hypercalcemia, a condition with too much calcium in the blood that causes nausea, vomiting, weakness, and kidney problems.
It’s essential to take only the recommended amount of Vitamin D if a healthcare provider advises.
FAQs
- What is the best way to get Vitamin D?
- The best way to get Vitamin D is through moderate sun exposure. However, supplements and Vitamin D-rich foods can also help maintain healthy levels.
- How much sun exposure is needed for Vitamin D?
- Most people need about 10-30 minutes of sun exposure a few times a week to produce sufficient Vitamin D. The amount required varies depending on skin tone, age, and location.
- Can you get vitamin D from foods?
- Certain foods, such as fatty fish, egg yolks, and fortified products (e.g., milk and orange juice), are good sources of Vitamin D.
- What happens if you don’t get enough vitamin D?
- A Vitamin D deficiency can lead to bone problems, such as rickets in children and osteoporosis in adults. It can also weaken the immune system and affect mood.
- Is Vitamin D supplementation safe?
- Vitamin D supplements are generally safe when taken at the recommended dosage. However, taking too much vitamin D can cause health problems.
Conclusion
vitamina d is essential for maintaining good health, especially bone strength and immune function. Although sunlight is the primary source of Vitamin d, you can also get it from certain foods and supplements. Understanding how much Vitamin D you need and ensuring you’re getting enough can help you avoid deficiency and its associated health risks.